Tri-State Home Inspections provides inspections and testing for methamphetamine.
- Meth can only be found with lab samples to be sure the home is free of meth residue
What is

Tri-State Home Inspections LLC Blog
Education is the key to success, the day a person feels they know everything they need, is the day failure begins
Tri-State Home Inspections provides inspections and testing for methamphetamine.
What is
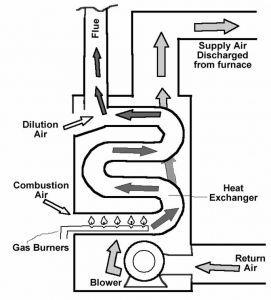
Forces air gas furnace is a central heating system used to heat a home or building. All furnaces work on the same basic principles and have similar parts:
The pilot light ignites a series of burners inside the combustion chamber that then enters the heat exchanger, where the heat transfers to the air in the home with the use of a fan to heat the home to the set point of the thermostat.
There are 3 types of forced gas furnaces I come across inspecting homes:
When looking at the efficiency it is easy to understand if you think in these terms:
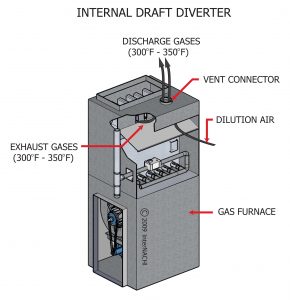
Low and Mid efficient furnaces have one heat exchanger usually 1 gas valve setting, and standard fan adjusted to one speed for heat, cool or just fan. They require a chimney to vent the flue gases to the exterior of the home, with temperatures of up to 300-350 degrees.
High efficiency condensing furnaces will have two heat exchangers, the standard heat exchanger as well as a second heat exchanger the flue gases are run though to extract as much heat from the system as possible. This process does cause condensation that is why they are called condensing furnaces. Because of the secondary heat exchanger these furnaces use PVC exhaust pipes with a temperature of about 100 degrees.

High efficient furnaces also come with several options to choose from to make the furnace even more efficient:
2-Statge gas valve
Variable Speed Motor (ECM) – This is the blower motor in the furnace, unlike the traditional motor is saves you money and adds to the comfort of your home:
With a high efficient furnace, I recommend to not turn the thermostat below 60 degrees because of the following possible results:
In the event that the furnace is not operating here are a couple recommendations to check before calling an HVAC specialist.